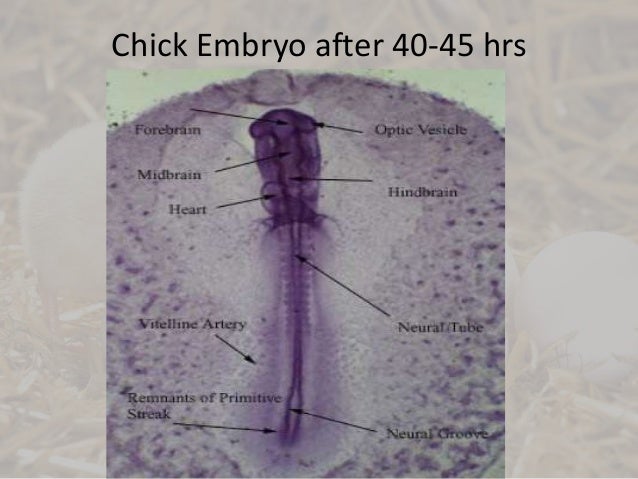
96 Hour Chick Embryo Serial Section
This page on the embryology in chicken relates to the following: • Whole mount preparation 72 hours, with a detail view on the development of the head () • Cross sections 72 hours; eye and heart formation ( ) Stage 72 hours Whole-mount preparation 72 hours after fertilization Information: 72 Hours after fertilization, the rotation of the embryo to the left is arrived such behind the region of the heart and only the caudal part of the embryo must twist 90 degrees. The two flexures in the head region are almost completed. The fourth pharyngeal groove develops and the pharyngeal arches are thicker. Due to the cranial flexure, the pharyngeal region (= region of the trachea) is now located at the ventral side of the head.
Start studying 96-Hour Chick Embryo. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools. Section between the origin of the lung buds and a point just anterior to the liver and pancreatic rudiments. The mesonephros may be seen at 72 hours and the metanephros at 96 hours. Portions give rise to gonoducts. Jan 05, 2012 Chicken: 72 h: This page on the embryology in chicken relates to the following. The rotation of the embryo to the left is arrived such behind the region of the heart and only the caudal part of the embryo must twist 90 degrees. The two flexures in the head region are almost completed. Left wholemount preparation and right cross section.
The fore and hind limbs at the level of the 16 th to the 20 th respectively the 27 th to the 32 th somite pairs are visible as small buds at an incubation time of about 3 days. Embryology of chicken 72 hours after fertilization: stained whole-mount preparation.
• You can only upload photos smaller than 5 MB. • You can only upload a photo (png, jpg, jpeg) or video (3gp, 3gpp, mp4, mov, avi, mpg, mpeg, rm). • You can only upload files of type 3GP, 3GPP, MP4, MOV, AVI, MPG, MPEG or RM. Kayamath star plus serial song download. • You can only upload videos smaller than 600 MB.

1 = Auditive (otic) vesicle, 2 = Myelencephalon, 3 = Metencephalon, 4 = Amnion, 5 = Mesencephalon, 6 = Optic vesicle + lens, 7 = Diencephalon, 8 = Epiphyse, 9 = Telencephalon, 10 = Branchial arches, 11 = Heart, 12 = Forelimb (wing) bud, 13 = Vitelline arteria/vein, 14 = Hindlimb (leg) bud, 15 = Tail Information: The development of the brain is shown at higher magnification. The further development of the five brain vesicles (telencephalon, diencephalon, metencephalon, mesencephalon and myencephalon) in to the different head structures is clearly visible. The eye vesicles differentiate as two lateral projections of the diencephalon and come in contact with the external layer (ectoderm) to form the optic cup (neurectoderm) and the lens (ectoderm). The dorsal projection of the dieencephalon is also visible and will differentiate in to the epiphysis (epi= at the upper side). The depression at the ventral side of the diencephalon develops in to the hypophysis ( hypo= under; not visible in this fig.). The auditory vesicles develop at the level of the myencephalon. Embryology of chicken 72 hours after fertilization: detail of the head in a stained wholemount preparation 1 = Auditive (otic) vesicle, 2 = Myelencephalon, 3 = Metencephalon, 4 = Amnion, 5 = Mesencephalon, 6 = Optic bulb, 7 = Lens, 8 = Diencephalon, 9 = Epiphyse, 10 = Telencephalon, 11 = Olfactory groove Cross sections 72 hours A.